Dzieła literatury angielskiej - lektury dla młodzieży i dorosłych po angielsku
Literatura angielska dla młodzieży i dorosłych - do czytania, słuchania i nauki angielskiego
Klasyka literatury angielskiej przeznaczone do czytania przez młodzież i dorosłych oraz słuchania w formie słuchowisk i audiobooków, wraz z ćwiczeniami i materiałami wspomagającymi naukę angielskiego, w tym rozumienie ze słuchu (listening) i naukę czytania (reading).
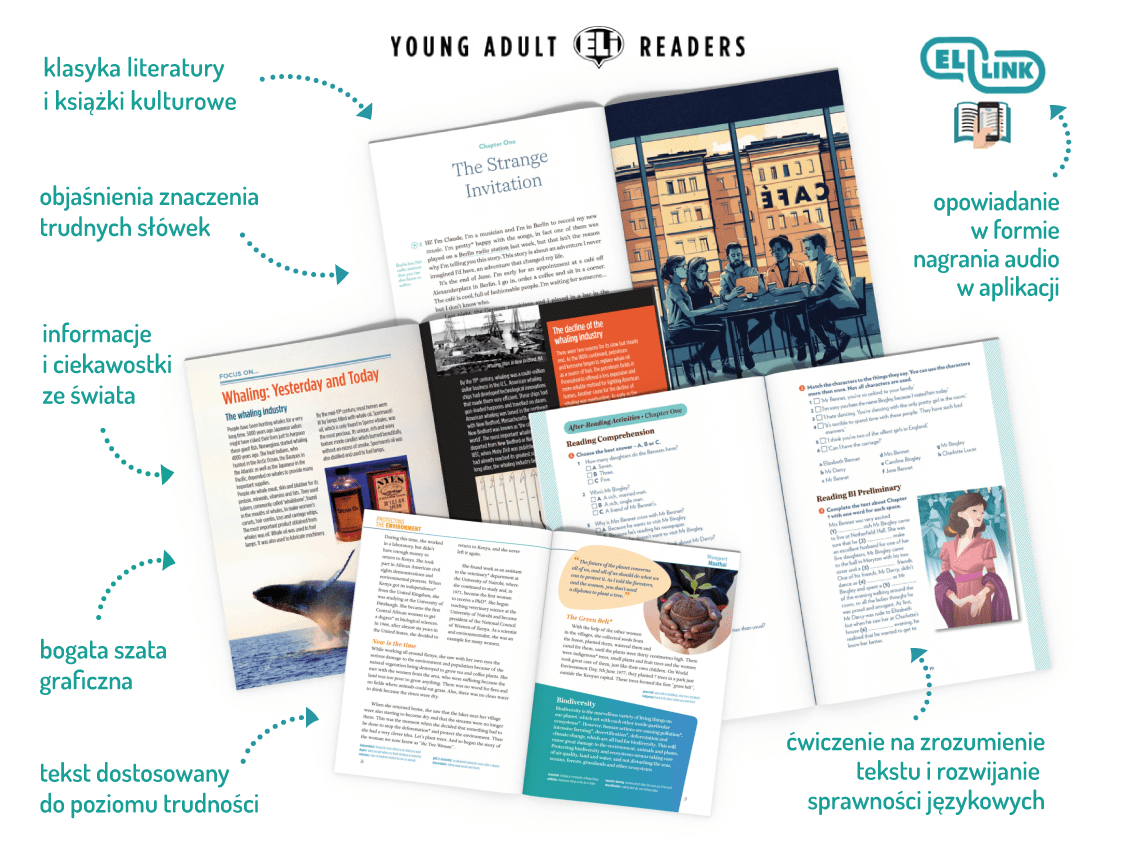
Książki napisane są uproszczonym językiem tak, aby były zrozumiałe dla czytelników na różnych poziomach znajomości języka angielskiego. Oryginalne stylistycznie ilustracje wykonane przez doświadczonych rysowników, a także ciekawa szata graficzna wspomagają poznawanie słownictwa i konstrukcji językowych. Doskonałe do nauki indywidualnej w celu doskonalenia znajomości języka i poznania dzieł literatury angielskiej.










Young Adult ELi Readers (A1-C2)
Młodzież i dorośli
Kluczowe informacje:
- Nauczany język: angielski
- Poziom trudności: A1-C2
- Ilość słów bazowych, z których zbudowany jest tekst: 600-2500 wzwyż
- Przedział wiekowy: młodzież i dorośli
- Przeznaczenie: w domu, na zajęciach
- Sposób wykorzystania: czytanie samodzielne lub z nauczycielem
Dlaczego warto sięgnąć po Young Adult Readers?
Informacje
Young Adult ELi Readers to seria adaptacji dzieł klasyki literatury anglojęzycznej w uproszczonych językowo wersjach lub w oryginale oraz książek poświęconych tematom kulturowym i popularnonaukowym. Książki oferują poziomy trudności językowej od A1 do C2 i przeznaczone są dla młodzieży i czytelników dorosłych.
Struktura książki:
Prezentowane historie podzielone są na rozdziały. Poprzedzone są sekcjami wprowadzającymi czytelnika w treść książki oraz w specyficzne słownictwo i gramatykę. W lepszym przyswojeniu tekstu pomagają objaśnienia znaczenia trudnych słów oraz ćwiczenia sprawdzające zrozumienie fabuły poszczególnych rozdziałów. Książki zawierają ponadto sekcje prezentujące ciekawostki historyczne i kulturowe związane z tematem książki lub danym dziełem literackim. Każdą lekturę zamykają ćwiczenia sprawdzające ogólny poziom zrozumienia i zapamiętania przeczytanej historii.
Książkom towarzyszą nagrania audio tekstu do odsłuchu za pomocą aplikacji ELiLink lub pobrania w formie plików.
Książki podzielone są na cztery następujące poziomy trudności:
- Stage 1 (600 headwords) Elementary A1 Movers
- Stage 2 (800 headwords) Pre-intermediate A2 Key
- Stage 3 (1000 headwords) Intermediate B1 Preliminary
- Stage 4 (1800 headwords) Upper Intermediate B2 First
- Stage 5 (2500 headwords) Advanced C1 Advanced
- Stage 6 Unabridged Texts Proficiency C2 Proficiency
Zawartość językowa:
Stage 1 (600 headwords) Elementary A1 Movers
Verb forms and tenses
Positive, negative, question and short answer forms including contractions
Positive and negative imperative forms
Present Simple
have got
there is/are
will for offers, requests and future meaning
Past Simple of regular and very common irregular verbs
can/can’t for ability, requests and permission
could (past form of can)
have to for obligation
would and wouldn’t like
Common phrasal verbs with transparent meanings
-ing forms after go
Sentence types
Two clauses joined with so, before, after, when
Direct speech + subject/verb inversion
Reported speech with present tense reporting verb
know, think, hope etc + that clause
Stage 2 (800 headwords) Pre-intermediate A2 Key
Verb tenses
Present Continuous
Past Simple of regular and irregular verbs
Past Continuous
Past continuous vs Past Simple
Future reference: Present Continuous, going to, will, shall, Present Simple
Present Perfect Simple: recent past with just, indefinite past with yet, already, ever, never, unfinished past with for and since
Present Perfect vs Past Simple
Modal verbs
could: ability, requests and suggestions
will: promises, predictions
would for desires, preferences
shall: suggestions, offers, plans
should (present and future reference):advice
may (present and future reference): possibility
must: personal obligation
mustn’t: prohibition
have (got) to: external obligation
need (to)/needn’t: necessity
Verb forms and patterns
Passive forms: Present Simple and Past Simple
Short questions (Can you?) and Short answers (No, he doesn’t)
Infinitives (with and without to) after verbs and adjectives
Gerunds after prepositions and verbs
Gerunds as subjects and objects
be able to
infinitive of purpose
Question tags
Common phrasal verbs with nontransparent meanings
so/neither/nor + auxiliaries in short answers
Sentence types
Main clause
Sentences with more than two main clauses
Sentences with one main and one subordinate clause
Subordination (in the Present Simple or Present Continuous) after verbs such as: be sure, know, think, believe, hope, say, tell
Subordination after: because, when, where
Co-ordination: but, and, or, and then
Zero and first conditionals
Defining relative clauses
Clauses with wh words
Clauses ending in so, not
Reported speech with to + infinitive
Participle clauses
Adjectives/nouns + that clause
Stage 3 (1000 headwords) Intermediate B1 Preliminary
Verb tenses
Present Perfect Simple: the first/ second etc. time that…
Present Perfect Simple: negative duration (haven’t ….for ages)
Past Perfect Simple: in reported speech and narrative
Modal verbs
can’t: logical necessity
could: ability (was able to/managed to,) possibility
may/can/could: permission
might (present and future reference): possibility, permission
must: logical necessity and obligation
don’t have to /haven’t got to /didn’t have to: lack of obligation
had to: obligation
would rather: preference
should: (present and future reference): moral obligation
ought to: (present and future reference): moral obligation
used to/would: past habits and states
Verb forms and patterns
Causative: have/get + object + past participle
make/let + infinitive
Past forms with going to and will
Verb + object + full infinitive (e.g. I want you to help.)
Verb + object + infinitive give/take/send/bring/show + direct/indirect object
be used to + ing
Simple reported speech: statements, questions and commands with say, ask, tell
Phrasal verbs/verbs with prepositions
had better
for advice or desirability
Sentence types
Complex sentences where the relations between clauses are uncomplicated
Non-defining relative clauses
Time clauses introduced by when, while, until, before, after, as soon as
Clauses of purpose: so that, (in order) to (infinitive of purpose)
First conditional with unless
Second conditional
Second conditional with wish
Clauses of result: so, so…that, such…. that
Clauses of concession: although, though
Stage 4 (1800 headwords) Upper Intermediate B2 First
Verbs
Present Perfect Continuous
Past Perfect Simple: negative duration (hadn’t ….for ages)
Past Perfect Continuous
Future Continuous
Future Perfect
Verb forms and patterns
Passive forms with all tenses
Passive forms with modal verbs
Phrasal verbs with non-transparent meanings
Reported speech introduced by precise reporting verbs (e.g. suggest, promise, apologise, threaten, insist,
complain)
It’s time + past tense
Modal verbs
would for willingness/refusal
modal perfects (must have, could have etc)
Sentence types
Embedded relative clauses
Third conditional
wish, if only
Mixed conditional sentences
Emphatic structures with what
Clauses of concession: even though, in spite of, despite
Complex sentences with more than one subordinate clause
Inversion after hardly, no sooner, not only
-ing/wh- clause as subject
Stage 5 (2500 headwords) Advanced C1 Advanced
Verb tenses
Future perfect continuous
Sentence types
Inversion in third conditional sentences without if
Inversion after other initial negative adverbs (at no time, little etc)
Inversion of subject and verb after adverbial expressions of place
Complex clauses with no restrictions on number of subordinate clauses
Stage 6 Unabridged Texts Proficiency C2 Proficiency
This stage contains the original, unabridged version of texts.
Materiały do pobrania ze strony elionline.com:
- nagrania audio (do pobrania i odsłuchu także za pośrednictwem aplikacji ELiLink),
- rozwiązania do ćwiczeń.
Materiału audio towarzyszącego każdej z książek słuchać można za pośrednictwem ELiLink. To prosta aplikacja smartfon lub tablet, z której korzystać może zarówno uczeń, nauczyciel, jak i indywidualny czytelnik. Umożliwia pobieranie i odsłuchiwanie nagrań audio. Pobranie multimediów następuje po zeskanowaniu telefonem strony z podręcznika. Nagrań zapisanych w urządzeniu słuchać możesz tak, jak klasycznego audiobooka.
Pobierz aplikację ELiLink: 

Pragniesz w pełni wykorzystać potencjał lektur do nauki języka?

W przypadku wykorzystania książek w pracy z grupą uczniów, bądź do indywidualnej nauki w domu, sięgnij po specjalny przewodnik pt. Jak skutecznie korzystać z lektur językowych? Książka ta, oprócz wyczerpującego opisu kolekcji, przybliża czytelnikowi całościową ideę pracy z tekstem oraz stanowi bogate źródło pomysłów przydatnych w nauczaniu języków obcych, w szczególności zaś przy użyciu metody czytania ekstensywnego. Publikacja zawiera również szereg interesujących uwag metodycznych, a także szczegółowo opisuje dodatkowe aktywności z tekstem, takie jak np. techniki dramatyczne, które z łatwością można zaadaptować i zmodyfikować wedle własnych potrzeb i celów dydaktycznych.
Przewodnik może okazać się ponadto przydatny dla osób samodzielnie uczących się języka obcego przy wykorzystaniu technik czytania ekstensywnego, gdyż wskazuje główne problemy napotykane podczas czytania w języku obcym i próbuje podać ich rozwiązania.
Książkę można zakupić lub otrzymać nieodpłatnie. Więcej na stronie ettoi.pl.
Zobacz przykładowe strony z książek z tej serii:
Przejrzyj tytuły i ceny
Przejdź do sklepu i przeglądaj lektury z tej serii oraz aktualne ceny!
